Inflammation is the leading cause of chronic disease in today’s society. Thankfully, there are various dietary and lifestyle changes we can make to help decrease inflammation in the body.
One change you can make is increasing daily intake of omega-3 anti-inflammatory fatty acids to balance out the fatty acid ratio in your body and therefore help manage inflammation.
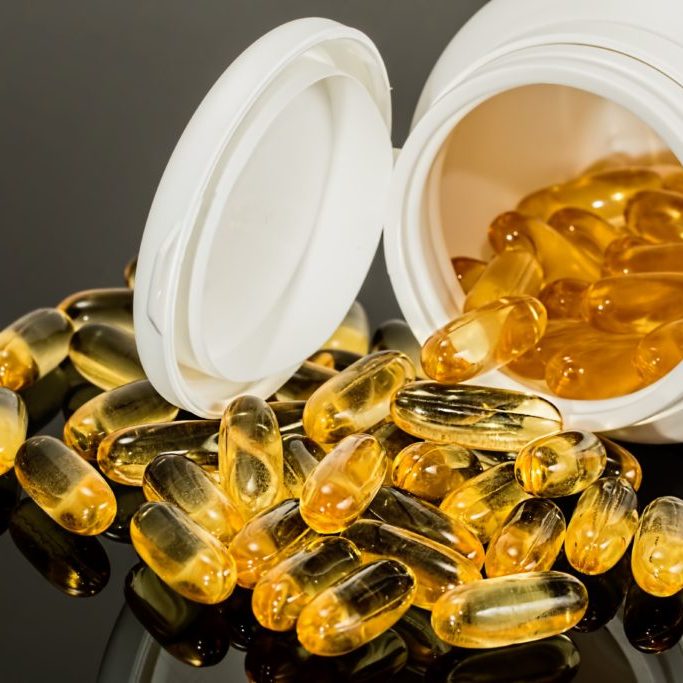
Fish oil is a common omega-3 supplement and is continuing to grow in popularity.
With the growing popularity of fish oil supplements comes a surge in supply and many different supplement options available. Some fish oil supplements are very low quality while others are third party tested and worth the extra cash. Some have a full 3g combined EPA and DHA, while others may only have half that in a dose.
So how do you choose a supplement or diet change that’s right for you? Is it worth the cost to add fish oil as a daily supplement? And what are the proven benefits of increasing omega-3 intake?
All valid questions you should be asking before popping those big yellow pills.
What are Omega-3s?
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of fat found in foods and in the human body. The two long chain forms of omega-3s are EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which are found in fish and shellfish.
ALA is another omega-3 that is a short chain fatty acid found in plants like flaxseed and chia seed. ALA is thought to be a less potent form of omega-3 and does not provide the same health benefits as EPA and DHA. The body will convert small amounts of ALA into the more powerful EPA and DHA.
EPA and DHA each have their own vital roles to play in the human body. Both have been linked to fetal development, cardiovascular health, and cognitive health. DHA is a true powerhouse in the body, a key component of all cell membranes.
While omega-3s are known as the anti-inflammatory fatty acids, omega-6s can actually be pro-inflammatory.
The Omega-6 to Omega-3 Ratio
One of the best reasons to take in omega-3s is to offset the cumulation of omega-6s from the Standard American Diet. Omega-6s are another type of fatty acid that is pro-inflammatory, found in almost all packaged foods like crackers, cookies, and corn-fed beef.
The optimal ratio will vary depending on your individual genetic makeup and lifestyle, but some research suggests a ratio of about 2:1 omega-6 to omega-3s. Unfortunately, that ratio for many people today who eat a standard Western diet is closer to 20:1. It’s therefore no surprise that many people struggle with inflammation and chronic disease.
These cheap omega-6 oils are unstable polyunsaturated fats that, when cooked at high heat, become oxidized. Oxidized omega-6s can cause inflammation in the body and damage DNA. A high omega-6 diet can lead to cardiovascular disease, cancer, and autoimmune diseases.
Having higher concentrations of omega-6s has also been correlated with sarcopenia, the loss of muscle tissue associated with aging. Balancing your omega-3 to omega-6 ratio may help the body resolve inflammation while also helping you get better gains in the gym and maintain muscle mass as you age.
The best way to increase amounts of EPA and DHA is through your diet. Foods high in omega-3s include fish & shellfish (especially fatty fish like salmon and sardines) as well as various nuts and seeds.
Health Benefits of Omega-3s
Research on fatty acids is ongoing; in fact it’s one of the most studied supplements on the market, which makes sense because by the time you finish this article you’re going to assume it’s a “wonder drug”.
Scientists have also studied many cultures that eat a high amount of seafood containing omega-3’s (who also happen to have lower risks for chronic disease) and therefore the amount of literature on omega-3’s as a nutrient, is even larger. Remember that in all literature, there is causation and correlation. Meaning we always need to dissect things, study a bit more and even use our own personal anecdote to make good decisions with our supplementation.
That being said, here’s the amazing list of benefits omega-3’s (fish oil) may be able to provide you with:
[If you’d rather listen to it, check out the podcast we did on all things fish oil – with “The Fish Guy”, Evan Demarco]
1.Cardiovascular Health
Fish oil is said to have protective heart benefits by reducing inflammation and triglyceride levels. One study showed that a high dose prescription of omega-3s staved off heart disease risk in already high risk patients. This doesn’t mean taking fish oil can prevent all cardiovascular decline, but it is promising for those people who are at risk for heart disease.
2. Cognitive Function
While there isn’t a clear link between fish oil and brain health, scientists have found those who eat a diet low in omega-3s may have higher risk for alzheimer’s. Additionally, one 2016 study suggested that eating fish once per week may protect against cognitive decline.
And although fish oil is not a stimulant, it does increase brain activity and that may cause a stimulatory effect after supplementing. In our experience, this occurs more often or is more noticeable once consistently taken over time which is exactly why we suggest it for individuals who have long work hours or need a creative mind for extended periods of time.
3. Reduced Inflammation
The role of omega-3s and inflammation has primarily been studied by looking at arthritis pain. When compared to ibuprofen in a study, omega-3s demonstrated “equivalent effect in reducing arthritic pain.” This suggests that fish oil may be a safer alternative to NSAIDs and help reduce overall inflammation in the body.
Anecdotally speaking, our coaching staff as well as our colleagues in the industry have seen great results from clients with joint pain and inflammation supplementing with omega-3 fish oils.
4. Depression Relief
Wait, what….?! Depression?
I know, it probably sounds like we’re reaching now but don’t worry – we don’t sell any supplements and aren’t affiliate with any either. But studies have actually shown, “fish oil supplementation has been noted to be comparable to pharmaceutical drugs (fluoxetine) in majorly depressed persons, but this may be the only cohort that experiences a reduction of depression. There is insufficient evidence to support a reduction of depressive symptoms in persons with minor depression (ie. not diagnosed major depressive disorder).”
So what does this mean? This means that if someone is truly suffering with clinical depression, this may be a healthier alternative to opt for than heavy pharmaceuticals. It also doesn’t necessarily mean that taking this as an average individual with average mood swings is going to make everything butterflies and unicorns every day, but in my personal opinion if there’s anything that may correlate to positive moods – it’s worth it, because in conjunction with a healthy lifestyle we’re extremely likely to have better moods, less depression, and likely less stress or anxiety.
5. Children’s Health
This is why you may see many prenatal supplements with DHA/EPA included in them, now. Or people like Dr. Rhonda Patrick supplementing with ultra-high doses of fish oils while she was recently pregnant and breastfeeding. One benefit is treatment of ADHD, “supplemental DHA above 300mg appears to be effective in reducing ADHD symptoms in children when supplemented.”
During pregnancy it’s smart to supplement with this for hormonal, neurological, and visual development for the baby. Add to that, it’s been shown to help increase birth weight of the child.
6. Blood Glucose and Insulin Sensitivity
This one is iffy, if we’re being honest. Here’s what Examine.com has to say, “No significant influence on insulin sensitivity seems to be the consensus, although there are isolated reports of both an increase and decrease (in response to a glucose tolerance test and fasting, respectively).”
So why even list this as a benefit? Mainly because there are isolated reports of increases, which may suggest that in combination with other healthy habits or influences it may have an effect. An example of this is that there has been reports that omega-3’s can increase muscle protein synthesis, but that would not happen without the combination of resistance training and protein consumption. However, if fish oil can help increase those 2 important benefits in the body – it’s worth it.
We’ve listed enough for fish oil to be worth taking so if there’s a 5-10% chance it could increase insulin sensitivity along with other healthy habits you’re practicing, it’s worth adding to the list!
7. Exercise Induced Oxidation
This has been noted to be increased in elite athletes with fish oil supplementation, but what does this mean for you?
It means that it may increase exercise induced oxidation in the body for you, too! The reality is that elite athletes who were in the study, but doesn’t mean we don’t receive the benefit from it as well. May it be lessened due to them being physical specimens? Very well so, but oxidation in the body is a positive process for both health and fat loss. So we’ll take it!
8. Body Recomposition
We use “recomp” lightly, because technically that means losing fat while building muscle – aka damn near impossible in majority of people. However we used this term here because we believe fish oil can help both fat loss and building muscle, not simultaneously but in the sense that both may be improved indirectly.
Physical results come from proper nutritional strategies and hard training; both which may be directly improved by supplementation of fish oil, mainly due to the inflammation benefits behind it. But the point here is simple, if you want to change your physique you shouldn’t skip out on fish oil.
9. Fat Oxidation
“An increase in fat oxidation (percentage of energy being taken from fat tissue) has been noted with fish oil supplementation.”
If we read that statement alone, we’re ALL IN on fish oil… but slow down, because it’s not that simple. The reality is that a.) you’re taking in more fats by consuming fish oil and therefore your body has more fats to burn, so fat oxidation increasing is a given and doesn’t directly mean you’re burning more fat from your body. And b.) this is more than likely majorly caused by correlation, meaning in combination with other healthy habits.
But the truths to this statement are a.) scientists did all the studies and put out this statement, which does give it merit. And b.) if your body becomes trained to be better at fat oxidation, it will burn more body fat when going into a diet and training hard. Which means this could be beneficial for future dieting.
10. Disease Prevention
This has been hinted at throughout the blog, but it’s worth adding in as its own standalone bullet point.
Fish oil has been shown to help prevent multiple diseases and autoimmune related illnesses. Is it because of the EPA/DHA? Is it simply an after-effective of the inflammation reduction fish oil causes? Is fish oil a super-food?!
We can’t be sure but we do know that science has proven this as fact and that means increasing your longevity and well-being, so it’s worth supplementing.
11. Balance Your Fatty Acid Ratio
Based on the science and literature available, ingesting additional omega-3s is clearly not a cure-all. However, it can help balance out your omega-6 to omega-3 ratio as discussed above. The ideal ratio for you will depend on a wide set of variables, but a lower ratio than that of most of Western culture (eating a diet high in processed foods) will help to reduce your risk of chronic disease.
This right here is the last bullet point for a reason; that reason being it’s the dominating key to the majority of health benefits omega-3’s possess. What we mean by this, is that you will get much more benefit from balancing your omega-3 to 6 ratio than you will by simply supplementing a fish oil capsule and completely ignoring your omega-6 intake.
Increasing Your Omega-3 Intake
Before you reach for those fish oil pills, remember that there is no magic pill that can solve all of your problems. First look at your current diet and lifestyle to see what changes you can make. Do you eat many fried foods? What about foods with long lists of ingredients and various oils?
We recommend looking at what you’re currently eating and seeing what changes you can make before relying on any supplement to be the band-aid on a poor diet.
If you want to experiment with making some diet changes and potentially add in a supplement, check out the following tips.
1.Eat More Fish
The best way to increase amounts of EPA and DHA is through your diet. Foods high in omega-3s include fish & shellfish, various nuts and seeds (like chia seeds and walnuts), and grass-fed beef.
If you want to up your fish intake, look for sustainably sourced fish that is low in mercury. Specifically if you are pregnant or nursing, you would want to avoid fish that are high on the food chain, which could have a higher accumulation of toxins.
The FDA has recommended to avoid eating shark, swordfish, king mackerel, or tilefish, all of which may contain high levels of mercury. Learn where the fish you’re eating are coming from to know that you’re consuming high quality food.
The American Heart Association recommends 2 servings of fish per week. Salmon and anchovies would be your best option at 1-2g omega-3 per serving, but omega-3 content will vary between fish species.
Pro Tip: Maybe you’ve heard of Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) shares at your local farmers market, but now there are even some fish CSA shares available like this one. Talk about connecting with your food source!
2. Cut Down on Omega-6s
If you choose to increase your intake of omega-3s, it would also behoove you to cut out foods high in omega-6 fatty acids like soybean, corn, sunflower, or safflower oils. This will help bring that omega-6 to omega-3 ratio back in balance (balance meaning they’re both important, however ~75% of US citizens are likely consuming too many 6’s and too little 3’s – we need both, but in the opposite balance as most currently have).
One great way to cut down on omega-6s is by doing more of your own cooking! When you eat at a restaurant, you never know how much oil or even what kind of oil your food is being cooked in. Avoid excess inflammatory oils by cooking more of your own meals at home.
For meal prep tips – read this next!
3. Supplement
Another option to increase your omega-3 intake is with a fish oil or krill oil supplement. Most studies have suggested taking 2-4 grams combined EPA & DHA per day.
When looking for a supplement, choose one that is third party tested for purity and sustainability (i.e. Friend of the Sea, Marine Stewardship Council, and NSF International).
Some fish oil supplements can be high in filler oils and low in actual EPA and DHA. Be sure to look at the nutrition facts on the supplement and see what percentage omega-3 is actually in the product. You want about 70% concentrate in the supplement. For example, if there’s 1 g of fish oil and 700mg of combined EPA & DHA, you’re probably getting a solid product.
Some fish oil supplements we recommend are Puori and Viva Naturals.
Krill oil is another supplement that may be even more bioavailable than fish oil, not to mention a more sustainable option. The fats in krill oil are phospholipids, instead of triglycerides as in fish oil, which can be used more immediately by the body. However, you will typically need more krill oil than fish oil, so be sure to look at the omega-3s per serving size on the label. And again, look for a quality supplement that is 100% krill oil like this one.
What about those fish oil burps?
If you are burping up fish oil after taking a supplement, chances are you either have a low quality supplement or you’re having trouble digesting the capsules.
Check your supplement quality first by doing the freezer test – put your fish oil supplement capsules in the freezer overnight. If they turn cloudy, your supplement might be high in omega-6 filler oils. If the capsules remain clear, you have a high quality supplement!
If you’re still getting the dreaded fish burps, try taking your supplement with a full meal. This should help your body digest the capsules more easily, being in full-on digestion mode. Another option is to try a liquid form of fish oil instead of a capsule.
I said it above and I’ll say it again, eating fish or adding in an omega-3 supplement is not a cure-all. As with most topics in the nutrition and fitness space, success is linked to dialing in the basics. Always start with diet and lifestyle changes, like eating mostly whole (not fried) foods and getting adequate exercise, to get manage inflammation in the body and keep your heart and brain healthy!
Resources
- https://examine.com/supplements/fish-oil/ – Curated list of most literature on fish oil
- “Omega-3 Supplements: In Depth” https://nccih.nih.gov/health/omega3/introduction.htm
- “Omega-3 Fatty Acids EPA and DHA: Health Benefits Throughout Life” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3262608/
- “Comparison of bioavailability of krill oil versus fish oil and health effect.”
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26357480
- https://www.nytimes.com/2018/09/25/well/fish-oil-heart-attack-stroke-triglycerides-omega-3s.html
- “APOE ε4 and the associations of seafood and long-chain omega-3 fatty acids with cognitive decline.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27164694
- “Omega-3 fatty acids (fish oil) as an anti-inflammatory: an alternative to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for discogenic pain.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16531187
- The Boom Boom Performance Podcast Ep. 220: Evan Demarco – The Science Behind Fish Oil & CBD Oil
This Blog was written in combination of Coach Caroline and Cody McBroom!
CLICK HERE NOW, TO APPLY FOR COACHING WITH ONE OF OUR COACHES!